Viral Infections in Humans - Poliovirus
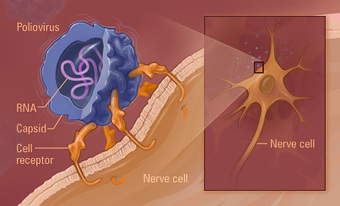
There are countless viruses that can infect humans and cause disease. The virus pictured to the left is the Poliovirus, one of the most simplest and well studied viruses consisting of a short RNA genome with an icosahedral capsid (protein coat) and no envelope. It is extremely small, with a diameter of about 30 nanometers. There are three types of poliovirus, Type 1, 2 and 3 (Type 1 being the most common and virulent).
Poliovirus is typically transmitted in food and water contaminated with the feces of infected people. The virus enters through the mouth and multiplies in the throat and gastrointestinal tract, then moves into the bloodstream and is carried to the central nervous system where it replicates and destroys the motor neuron cells. Motor neurons control the muscles for swallowing, circulation, respiration, and the trunk, arms, and legs. The infection process of poliovirus is illustrated below:
Poliovirus is typically transmitted in food and water contaminated with the feces of infected people. The virus enters through the mouth and multiplies in the throat and gastrointestinal tract, then moves into the bloodstream and is carried to the central nervous system where it replicates and destroys the motor neuron cells. Motor neurons control the muscles for swallowing, circulation, respiration, and the trunk, arms, and legs. The infection process of poliovirus is illustrated below:
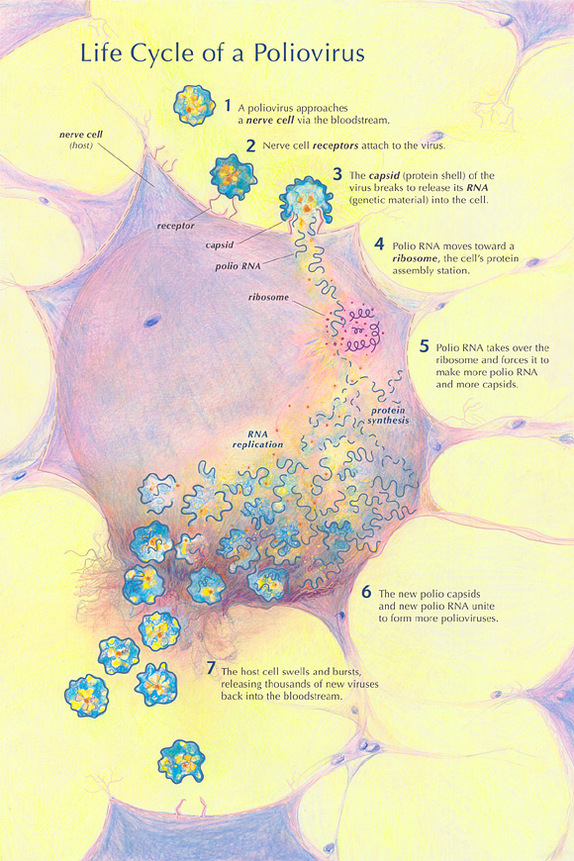
- Only 1 of 200 or so virus particles that encounter a susceptible nerve cell will successfully enter and replicate.
- In tissue culture, poliovirus enters cells and replicates in six to eight hours, yielding 10,000 to 100,000 virus particles per cell.
- The disease caused by infection of the poliovirus is known as Poliomyelitis, which is an acute inflammatory process marked by symptoms of "fever, pains, and gastroenteric disturbances, followed by a flaccid paralysis of one or more muscular groups, and later by atrophy." -Stedman’s Medical Dictionary, 1995.
- Polio may also be diagnosed through other symptoms, such as stiff neck and back, trouble breathing, or nausea.
Treatments and Prevention? Poliomyelitis is not a treatable disease - that is there are no cures for it - and the only treatment possible involves improving a persons chance of recovery. Symptoms can also be treated and discomfort alleviated while a person recovers.
Polio is completely preventable however, with vaccination providing the most effective form of prevention. Childhood immunization programs protect society from infection by the poliovirus.
Polio is completely preventable however, with vaccination providing the most effective form of prevention. Childhood immunization programs protect society from infection by the poliovirus.